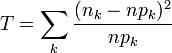|
|
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown) |
| Line 2: |
Line 2: |
| | '''Statistical hypotheses testing''' (5 pkt.) | | '''Statistical hypotheses testing''' (5 pkt.) |
| | | | |
| - | * The experiment of irradiating a hydrogen bubble chamber with a beam of photons was carried out in order to study the interaction of photons with protons. Photons create electron-positron pairs that can be used to monitor the photon beam. The frequency of images with 0,1,2, ... electron-positron pairs should follow the Poisson distribution. Data should be read from the [http://www.if.pw.edu.pl/~lgraczyk/KADD2016/lab10/dane10.txt file] (the first column shows the number of electron pairs in the image <code>k</code>, and the second column shows the number of photos containing <code>k</code> electron pairs). We can see that this distribution resembles the Poisson distribution - therefore we are trying to calculate the maximum likelihood estimator for the parameters of the Poisson distribution (see [http://www.if.pw.edu.pl/~lgraczyk/KADD2022/Wyklad10-2019.pdf Lecture 10]) (1 pkt.) | + | * The experiment of irradiating a hydrogen bubble chamber with a beam of photons was carried out in order to study the interaction of photons with protons. Photons create electron-positron pairs that can be used to monitor the photon beam. The frequency of images with 0,1,2, ... electron-positron pairs should follow the Poisson distribution. Data should be read from the [http://www.if.pw.edu.pl/~lgraczyk/KADD2016/lab10/dane10.txt file] (the first column shows the number of electron pairs in the image <code>k</code>, and the second column shows the number of photos containing <code>k</code> electron pairs). We can see that this distribution resembles the Poisson distribution - therefore we are trying to calculate the maximum likelihood estimator for the parameters of the Poisson distribution (see [http://www.if.pw.edu.pl/~lgraczyk/KADD2022/Wyklad10-2022.pdf Lecture 10]) (1 pkt.) |
| | | | |
| | * Narysować na jednym wykresie punkty pomiarowe i dopasowanie (metodą estymatora największej wiarygodności i funkcją Fit z ROOT'a użytą z parametrami "LR" - dopasowanie metodą największej wiarygodności). Funkcja TF1 do rysowania (i dopasowania ROOT'em) to TMath::PoissonI (1 pkt.) | | * Narysować na jednym wykresie punkty pomiarowe i dopasowanie (metodą estymatora największej wiarygodności i funkcją Fit z ROOT'a użytą z parametrami "LR" - dopasowanie metodą największej wiarygodności). Funkcja TF1 do rysowania (i dopasowania ROOT'em) to TMath::PoissonI (1 pkt.) |
| | | | |
| - | * Sprawdzić jakość dopasowania za pomocą testu χ2. W tym celu należy zaimplementować funkcję obliczającą statystykę testową χ2 zgodnie z wzorem [[File:wzor.png]] | + | * Check the quality of the fit with the χ2 test. For this purpose, a function for calculating the χ2 test statistic should be implemented according to the formul [[File:wzor.png]] |
| - | gdzie: nk - liczba obserwacji w k-tym binie, npk - przewidywana przez teorię liczba przypadków w k-tym binie tj.:
| + | where: nk - number of observations in the kth bin, npk - the number of cases predicted by the theory in the kth bin, i.e .: |
| | | | |
| - | // h - histogram danych | + | // h - data histogram |
| - | // g - przewidywanie "teoretyczne" | + | // g - "theoretical" prediction |
| | double chi2(TH1D *h, TF1 *f); | | double chi2(TH1D *h, TF1 *f); |
| | | | |
| - | * Okreslić liczbę stopni swobody i obliczyć wartość statystyki testowej. (1 pkt.) | + | * Determine the number of degrees of freedom and calculate the value of the test statistic. (1 pt) |
| | | | |
| - | * Zaimplementować funkcję zwracającą wynik testu χ2 na zadanym poziomie istotności α tj.: | + | * Implement a function that returns the result of the χ2 test at a given significance level α, i.e .: |
| - | // true - brak podstaw do odrzucenia hipotezy
| + | // true - there is no reason to reject the hypothesis |
| - | // false - sa podstawy do odrzucenia hipotezy
| + | // false - there are grounds for rejecting the hypothesis |
| - | // Parametry:
| + | // Parameters: |
| - | // T - wartosc statystyki testowej chi2
| + | // T - value of the chi2 test statistic |
| - | // alpha - poziom istotnosci
| + | // alpha - significance level |
| - | // ndf - liczba stopni swobody rozkladu chi2
| + | // ndf - the number of degrees of freedom of chi2 distribution |
| | bool testChi2(double T, double alpha, int ndf); | | bool testChi2(double T, double alpha, int ndf); |
| | | | |
| - | Wykorzystując zaimplementowaną funkcję zweryfikować hipotezę mówiacą, że dane pomiarowe podlegają rozkładowi Poissona. Dobrać odpowiednią wartość poziomu istotności. Uwaga! Kwanyl możemy odczytać z policzonej na ostatnich zajęciach dystrybuanty. (2 pkt.)
| + | Using the implemented function, verify the hypothesis that the measurement data are subject to the Poisson distribution. Select the appropriate value for the significance level. Warning! Kwanyl can be read from the distribution box counted in the last class. (2 pts) |
| | | | |
| | == Attention == | | == Attention == |
| - | * Nasze zadanie to '''ręczne''' przeprowadzenie czynności wykonywanych automatycznie przez funkcję <code>Fit</code>. | + | * Our task is to ''manually'' carry out the actions performed automatically by the <code> Fit </code> function. |
| - | * Zadanie zawiera w sobie dwie części: wyznaczenie parametru rozkładu Poissona '''metodą największej wiarygodności''' (maximum likelihood), szukając '''estymatora o najniższej wariancji'''. Czytamy zatem: Wykład 9 [http://www.if.pw.edu.pl/~lgraczyk/KADD2019/Wyklad9-2019.pdf link] - o metodzie największej wiarygodności, od początku do slajdu 24 (to są części teoretyczne z wyprowadzeniami), dalej Wykład 10 [http://www.if.pw.edu.pl/~lgraczyk/KADD2019/Wyklad10-2019.pdf link] | + | * The problem consists of two parts: determining the parameter of the Poisson distribution ''by the maximum likelihood method'', looking for the ''estimator with the lowest variance''. So we read: Lecture 10 [http://www.if.pw.edu.pl/~lgraczyk/KADD2022/Wyklad10-2022.pdf link] - about the maximum likelihood method for Poissonian distribution |
| - | * Funkcja wiarygodności to ogólnie rzecz biorąc funkcja rozkładu prawdopodobieństwa dla '''parametrów''' badanego rozkładu, okreslana na podstawie próby losowej (jeżeli badamy np. rozkład wzrostu Polaków f(x), gdzie X to zmienna losowa okreslająca wzrost Polaków, np. rozkład Gaussa o dwóch parametrach (średnia, odchylenie), to L będzie funkcją wiarygodności, rozkładem prawdopodobieństwa parametrów średniej i odchylenia -> szukamy maksimum funkcji L, które da nam najbardziej wiarygodne wartości parametrów średnia i odchylenie funkcji f(x)) | + | * The likelihood function is, in general, a probability distribution function for the ''parameters'' of the analyzed distribution, determined on the basis of a random sample (if, for example, we study the growth distribution of Poles f (x), where X is a random variable determining the height of Poles, e.g. Gaussian distribution with two parameters (mean, deviation), then L will be the likelihood function, probability distribution of the parameters of the mean and deviation -> we are looking for the maximum of the L function, which will give us the most reliable values of the parameters mean and deviation of the function f (x)) |
| - | * Szukanie parametrów metodą największej wiarygodności polega na rozwiązaniu równań wiarygodności, które są niczym innym tylko warunkami koniecznymi na istnienie maksimum funkcji L (zgodnie z analizą matematyczna - liczymy odpowiednie pochodne) | + | * Searching for parameters using the maximum likelihood method consists in solving the likelihood equations, which are nothing more than the conditions necessary for the existence of the maximum of the L function (according to the mathematical analysis - we calculate the appropriate derivatives) |
| - | * Dla rozkładu Poissona estymator o najniższej wariancji otrzymany metodą największej wiarygodności wynika z rozwiązania równania wiarygodności (jedno równanie, bo jeden parametr Lambda) - slajd 14 na Wykładzie 11 [http://www.if.pw.edu.pl/~lgraczyk/KADD2019/Wyklad11-2019.pdf link] | + | * For the Poisson distribution, the estimator with the lowest variance obtained by the maximum likelihood method results from the solution of the likelihood equation (one equation, because one Lambda parameter) [http://www.if.pw.edu.pl/~lgraczyk/ KADD2022 / Wyklad10-2022.pdf link] |
| - | * Druga część, po znalezieniu estymatora o najwyższej wiarygodności, polega na przeprowadzeniu testu chi-kwadrat. W tym celu czytamy dokładnie Wykład 11 (zwłaszcza slajdy 7-16) [http://www.if.pw.edu.pl/~lgraczyk/KADD2019/Wyklad11-2019.pdf link]. | + | * The second part, after finding the estimator with the highest likelihood, is to perform a chi-square test. For this purpose, we read carefully Lecture 10 |
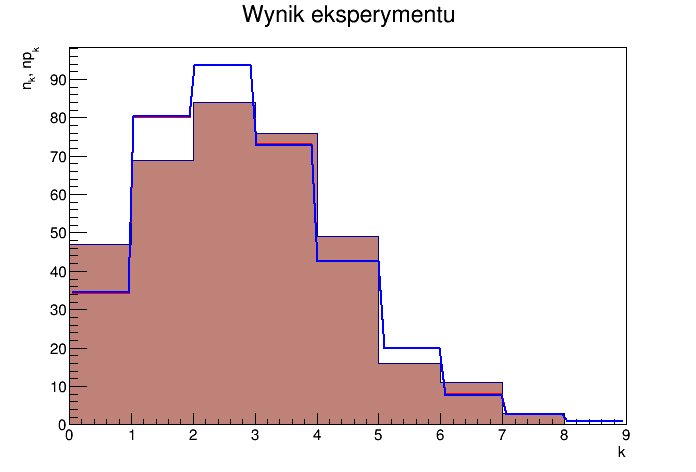
| - | * Na wykresie poniżej (histogram) są dwie linie - niebieska i czerwona. Jedna z nich to dopasowanie dokonane automatycznie funkcją <code>Fit</code>, druga to ręczne dopasowanie sposeb powyżej. | + | * There are two lines in the graph below (histogram) - blue and red. One is an auto-fit with <code> Fit </code>, the other is a manual procedure described above. |
| - | * Do rozkładu Poissona w postaci takich "schodków" stosujemy funkcję <code>TMath::PoissonI</code> ([https://root.cern.ch/root/html534/TMath.html#TMath:PoissonI link]) | + | * For the Poisson distribution in the form of such "steps" we use the function <code> TMath :: PoissonI </code> ([https://root.cern.ch/root/html534/TMath.html#TMath:PoissonI link]) |
| - | * Kwantyl rozkładu chi-kwadrat o odpowiedniej liczbie stopni swobody do wykonania testu możemy odczytać z '''Zadania 9''' (poprzednie zajęcia) - po to żeśmy te rozkłady chi-kwadrat rysowali. | + | * The quantile of the chi-square distribution with the appropriate number of degrees of freedom to perform the test can be read from Exercise 9 (previous classes) - that is why we drew these chi-square distributions last time. |
| | | | |
| | == Result == | | == Result == |
where: nk - number of observations in the kth bin, npk - the number of cases predicted by the theory in the kth bin, i.e .:
Using the implemented function, verify the hypothesis that the measurement data are subject to the Poisson distribution. Select the appropriate value for the significance level. Warning! Kwanyl can be read from the distribution box counted in the last class. (2 pts)